HOW WE GET IT DONE
GeoGym's approach to getting results!

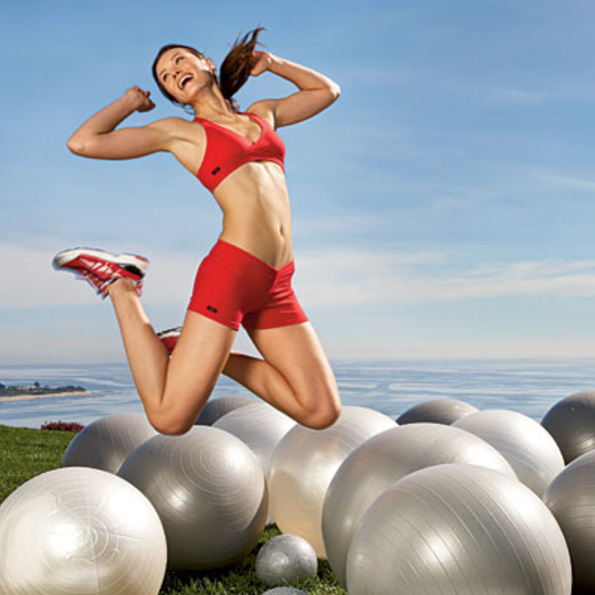
Cross Training and Interval Training are at the core of how we get results at GeoGym.
What is Cross Training?
Most simply, it is the rotation of several fitness activities either on different exercise days or during one exercise session. IE Alternate between activities during the week power walk one day, run the next, bike the next. You can also alternate activities within a single workout. IE Walking stairs, jumping rope, and jogging for 15 minutes each. Circuit training is a form of cross training, which combines cardiovascular activity sets with strength training sets during the same exercise session. This technique is great at developing deep aerobic capacity and muscle endurance/strength. Cross training offers you a refreshing physical and mental challenge!
Why is Cross Training Important?
When you begin an exercise program, the results are often obvious. You feel great, you begin to lose weight and your cloths fit a bit looser. Your workout performance improves. However, after a while, doing the same workout at the same intensity doesn't continue to produce results. You may begin to lose your enjoyment of the program as well. What happened?? You have reached a training plateau and it's time for a change! Cross training with GeoGym is one option to get you going again. Some of the documented benefits of cross training are:
Reduced Risk of Injury
By spreading the level of body stress over additional muscles and joints, you are able to exercise more frequently and for longer durations without excessively overloading particularly vulnerable areas of the body, such as knees, hips, back and feet. You may want to consider cross training between low-impact (swimming) and high-impact (running) activities. Another consideration is the movement patern. For example, you might cross train between swimming ,which usea a considerable proportion of upper body muscles and is non-impact and walking, which is a low impact lower body muscle activity. Remember, when starting a new activity, limit your first few sessions to train your body to adjust to the new activity. Once your body is "taught" the new activity, you can make this activity the same length of time as your previous training activity.
Enhanced Weight Loss
Individuals who want to lose weight and body fat should engage in an exercise program that enables hem to safely burn a significant number of calories. This is best accomplished when one exercises for relatively long durations (45-60 minutes) at a moderate level of intensity ( 60-80 % of maximal heart rate) most days of the week. Those who are overweight can effectively achieve a reduction in body weight and fat stores by combining two or more physical activities in a cross training program.
Improved total Fitness
Cross training can include activities that develop muscular fitness, as well as aerobic conditioning. While an individuals muscular fitness gains will typically be less than if one participated only in strength training, the added benefits of improving muscular strength and endurance can pay substantial dividends. For example, research has shown that resistance training can help to prevent injuries, control body weight and improve functional capacity.
Enhanced Exercise Adherence
Research on exercise adherence indicates that many individuals drop out of exercise programs because they become bored or injured. Cross training is safe and easy way to add variety to an exercise program. In the process, it can play a positive roll in promoting long-term exercise adherence by reducing the incidence of injury and eliminating or diminishing the potential for boredom.
What is Interval Training?
Interval training is simply short bursts of high-speed/intensity work followed by periods of rest of low intensity activity. Examples include incorporating periods of sprinting into a jogging workout or alternating leisurely walking with periods of faster walking. Intercal training is the easiest and most effective way to incorporate high-intensity exercise into any exercise program. The key is to choose exercises that use large muscles, are done in a way that is boimechanically correct and will get the heart pumping to increase maximal oxygen consumption.
Why is Interval Training Important?
For people trying to lose body fat, interval training is an effective exercise approach. To many people trying to shed fat believe that working out for longer periods of time in the mythical "fat burning zone" will lead to more fat loss. In reality, adding more time to a lower intensity cardio workout only makes the body more efficient at that intensity; it doesn't work the body harder as desired. Longer and longer bouts of low-intensity cardio hit a point of diminishing return, when burning fat is the goal. Higher intensity exercise stimulates your metabolism more after a workout than lower intensity exercise. This causes you to burn calories and fat for a longer period of time following your workout. Research shows interval training can have a positive impact on post-exercise caloric expenditure.
For those who say they don't have time to work out, interval training is a way to overcome this obstacle. Shorter workout sessions including interval training have been shown to have the benefit as longer, moderate paced sessions.
Interval training adds variety to a weekly exercise plan thereby reducing boredom and increasing exercise adherence.
Slow down aging with interval training. As we age, our hearts beat more slowly and pump less blood. Our lung capacity also decreases. These changes result ion decreased maximal consumption, which causes less oxygen to reach muscles. Oxygen is the life fuel for muscles; without it, they simply cannot work. This decrease in muscle oxygen consumption is one of the main reasons why we slow down, grow weak and lose stamina as we age. We cannot to the basic activities of daily living that allow us to enjoy life, maintain health and remain independent. Maximal oxygen consumption begins to decrease between 50 and 60 years of age, with the greatest decreases occurring after age 60. Regular, high intensity exercise can slow aging my more than a decade. Interval training is one of the most effective ways to exercise at a high enough intensity to significantly increase oxygen demands and ultimately slow aging.
What to know before starting interval training
Age and Weight Aging is associated with many changes in the body that influence how intensely person can exercise. Age-related musculoskeletal changes include decreases in muscle mass, joint cartilage, bone mineral density, and elasticity of tendons and ligaments. Because of persons over 40 show some sign of degenerative joint disease, individuals must bear these changes in mind and choose exercise that minimizes the joint stress.
Gender Woman over the age of 55 are the population most susceptible to injury from high-impact activities due to the general loss in bone mineral density associated with aging. It is important to know your own health history and to choose interval training programs that are appropriate for your joint and bone health.
Motor coordination and balance Typically, to increase the intensity of an exercise, the movement will become more difficult, requiring total body coordination, greater core work and better balance. It is important to choose interval training programs that are appropriate for your present coordination, balance ability and core strength.
.
|
|

|
|
CLASS SCHEDULE

|
|

|

 Become An Affiliate
Become An Affiliate
 Contact
Contact

 Become An Affiliate
Become An Affiliate
 Contact
Contact